Introduction There has been a considerable effort in recent years towards the preparation of new materials containing polyfunctional units (ligands) able to bind metallic ions. The Schiff base macroligands [1-6] are synthesized from the reaction of dialdehydes and amino compounds. Given that these materials form stable complexes, they provide the opportunity to design new systems selective to specific metallic ions. These materials could be applied in different areas such as electrochemistry, bioinorganic, catalysis, metallic deactivators, separation processes and environmental chemistry among others [7-9]. New Schiff base [2, 4, 10-11] macroligands have been synthesized to study their selectivity towards complexation of different metallic ions. These newly synthesized compounds are also used as precursors for the formation of other acyclic and cyclic ligands. Complexes of Schiff base ligands with structural similarities to phtalocyanines (N4-macrocycles) [7, 12-14], and other related compounds [15-20], are currently used as modifiers of the active surface of electrodes to improve their catalytic activity in the selective detection of organic pollutants [15, 21-24] and the entrainment of metals. Along the same line, our interest is to evaluate the capability of N,N’-bis(2-nitrobenzyl)ethylendiimine L1 (Figure 1), to bind diverse metallic ions such as Ni(II) and Co(II), and carry out selectivity studies. These complexes are later studied to test their potential in the development of chemically modified electrodes for use in pollutant detection. | 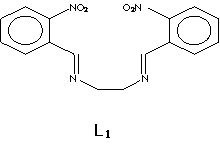
| | Figure 1. Structural Formula of the ligand N,N’-bis(2-nitrobenzyl)ethylendiimine (L1). | The selectivity studies showed that the complex [NiL1]SO4 is very stable at Standard temperature and pressure. It is currently being tested as a possible modifier of the active surface of an electrode. Under certain specific conditions this compound has been electrochemically polymerized over a vitreous carbon (VC) surface and over a glass surface covered with indium tin oxide (ITO) respectively. These chemically modified electrodes are being tested for the detection and degradation of organochlorinated pollutants. Experimental All the reactants used to obtain the ligands and their corresponding complexes were analytic grade from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company Inc, USA. Synthesis of N,N´-Bis(2-nitrobenzyl)ethylendiimine (L1) L1 was obtained by a condensation of a Schiff base according to a procedure previously reported, [3]. The nature of this compound was probed by infrared (IR) spectroscopy, and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and by melting point. Complexation reaction The ligand L1 was mixed directly in a refluxing solution with Co(II) and Ni(II) sulfates in equimolar amounts in acetonitrile. The corresponding complexes were characterized by IR spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis. The IR spectrum of the ligand shows a band at 1637 cm-1 corresponding to the imine group. The spectra of the complexes Ni(II)-L1 and Co(II)-L1 are consistent with the presence of the imine group showing the same band. It was also observed a shift of the bands corresponding to nitro groups along with a decrease in their intensity. This displacement suggests the presence of a heteroatom-M bond. The spectra also show an intense band around 1080 cm-1 corresponding to the sulfate ion. A solution of Ba(II) and Pb(II) was added to both complexes and an instantaneous precipitation occurred, suggesting that the sulfate ion is outside of the coordination sphere. Measurement of the Equilibrium Constants The formation constants for the complexes of Ni(II) and Co(II) with L1 were determined by conductimetry. Conductivities were measured for a series of solutions of each complex using an Orion conductimeter model 162. The formation constants are expressed in molar concentration at 25oC. Modification of Electrodes The electrochemical studies of the complex [Ni(II)- L1]SO4 were performed with a conventional three-electrodic potentiostatic system (CV-50W/ LG-50) (BAS)). The working electrodes were either a vitreous carbon electrode (VC) (BAS) of 3 mm diameter polished prior to all experiments, or an indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode. The potentials were measured with reference to the Ag/AgCl(s), KCl (BAS) electrode, placed in a compartment containing the supporting electrolyte. All the experiments were performed at room temperature. Table 1. Infrared data for N,N’-bis(2-nitrobenzyl)ethylendiimine (L1), [NiL1]SO4 and [CoL1]SO4. | | | | | | | L1 | 1335 , 1516 (s) | 1637 | Absent | Absent | | Ni-L1 | 1350 , 1530 (w) | 1630 | Absent | 1080 | | Co-L1 | 1347-1527 (w) | 1637 | Absent | 1130 | Results and Discussion The ligand L1 was obtained as yellow crystals with 83% yield. This yield was higher than the results reported in the literature [3]. The nature of the ligand was established using IR and NMR spectroscopy as well as analysis of monocrystal X- ray diffraction. The results of the IR analysis verify that the condensation reaction of the Schiff base was successful. The previous assumption was based on the presence of bands corresponding to the imine group at 1637 and the nitro group at 1335 and 1516 cm-1 as well as absence of the characteristic signals of the carbonyl and amine L1 groups, as can be seen in Table 1. The spectrum 1H NMR of the diimine ligand (L1) presents signals in the interval of 8.75-8.85 ppm corresponding to CH=N. This signal proves the integrity of the product. (Figure 2). The resonance data of the ligand are consistent with the proposed structure. | 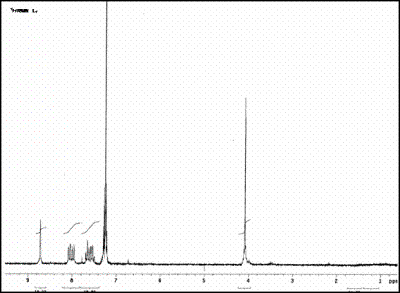
| | Figure 2. 1H NMR spectrum for N,N’-bis(2-nitrobenzyl)ethylendiimine (L1). | A single crystal of L1 for XRD studies was obtained. The Figure 3 shows the molecular structure of L1, it belongs to the monoclinic system. The Crystallographic data for L1 is reported in Table 2. | 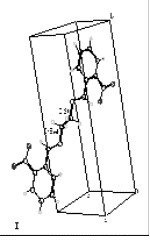
| | Figure 3. Monoclinic structure of L1 determined by monocrystal X-Ray diffraction. | The interaction of Ni(II) and Co(II) with the ligand L1 was investigated. The complexes were obtained from direct reaction between the metallic ions and the ligand using acetonitrile as solvent. The compounds showed different colors and were obtained with a 45 - 48% yield. Table 2. Crystal data for N,N’-bis(2-nitrobenzyl)ethylendiimine (L1). | Empirical formula | C8H7N2O2 | | Color and shape | Yellow, prismatic | | Crystal size | 0.36 x 0.20 x 0.12 mm | | Crystal system | Monoclínico | | Space group | P21/c | | Unit cell dimensions | a =7.4290(10) Å b= 15.503(2) Å c= 7.083(10) Å a= 90.00o b= 108.65o g= 90.00o | | Volumen (U/ Å3) | 772.93(18) | | Formula weight | 652.622 | | Density (calculated) | 1.402 mg/m3 | With respect to the IR data for the complexes, they were consistent with the presence of the imine group. Each complex exhibited a band between 1630 and 1637 cm-1. A shift and an intensity decrease of the bands of the nitro groups could also be observed. This suggests the presence of a heteroatom-M bond. The spectra also showed a band between 1080 and 1130 cm-1 which corresponds to the sulfate ion. The instantaneous precipitation of the sulfate ions upon addition a solution of Ba(II) and Pb(II) suggests that the sulfate is outside of the coordination sphere. The selectivity studies were carried out by atomic absorption. Table 3 shows the results which illustrates the preferences of the ligand to Ni(II) and Co(II) ions. Table 3. Selectivity Studies of the ligand L1 toward the Co(II) and Ni(II) ions determined by Atomic Absorption. | | | | | | [NiL1]SO4 | Blue. | 2.44 | [NiL1]SO4 | | [CoL1]SO4 | Light pink | 3.88 | [CoL1]SO4 | The conductimetric analysis for the complexes (shown in Tables 4 and 5) provide Kf = 1.25 x 106 for [NiL1]SO4 and 5.6 x 105 for [CoL1]SO4, these values show that the Ni(II) complex is slightly more stable than Co(II) complex. The results are in agreement with the stability reported in the literature for a series of complexes of Ni(II) and Co(II) based on their ionic radius [25]. A change of color at 87oC was observed while measuring the melting point of Ni(II)-L1 complex. This temperature is lower than 100oC, therefore one could think that such change in color is the result of the loss of non-essential water (hygroscopic or hydration type). The compound remained stable until 300oC where it begins to decompose. Table 4. Determination of the Formation Constant of [NiL1]SO4 by Conductimetry. | | | | | | | 5x10-4 | 1180 | 2360 | 1.18 | 4.24x10-4 | | 2x10-4 | 930 | 4650 | 0.93 | 2.15x10-4 | | 8x10-5 | 650 | 8125 | 0.65 | 1.23x10-4 | | 3x10-5 | 420 | 14000 | 0.42 | 7.14x10-5 | | 2x10-6 | 350 | 175000 | 0.35 | 5.71x10-6 | Kf = 1.25x106 Table 5. Determination of the Formation Constant of [CoL1]SO4 by Conductimetry. | | | | | | | 2x10-4 | 2300 | 4600 | 2.3 | 2.174*10-5 | | 4x10-5 | 1180 | 2360 | 1.18 | 2.119*10-5 | | 8x10-6 | 930 | 4650 | 0.93 | 1.344*10-5 | | 2x10-6 | 650 | 8125 | 0.65 | 9.615*10-6 | Kf = 5.60 x105 The thermograms from thermal studies performed on the complex [Ni(II)-L]SO4 are shown in Figure 4. These results show a loss of weight at approximately 90oC and also an endothermal peak at the same temperature. It can be thought that the complex loses hygroscopic and/or crystallization water at around 90oC (i.e. not directly bonded to the central metal ion). Latter can be demonstrated with the color changes of the compound, that it was due to the loss of water molecules. | ![AZoJomo - The AZO Journal of Materials Online - Thermograms of the complex [Ni(II)-L1]SO4](http://www.azom.com/work/D59B4p6gjqU0Hqxh2qa1_files/image007.gif)
| | Figure 4. Thermograms of the complex [Ni(II)-L1]SO4. | The alternatives previously mentioned for the case of the complex [Ni(II)-L1]SO4 could be possible because the Ni can form stable complexes acting with a coordination number of 4 or 6. Nevertheless, the chances of the water being coordinated at that temperature where the loss of weight occurs, are very small. Electrochemical studies were carried out on the complex [NiL1]SO4 and it was possible to polymerize this compound on the surface of vitreous carbon (VC), and indium tin oxide (ITO) electrodes. The studies were made using cyclic voltammetry in sweeps of 30 cycles. The chemical modification on the surface of the electrodes was proved by the presence of oxidation and reduction peaks which are characteristic of the Ni2+/Ni3+ redox pair. Different conditions were tested regarding sweep velocity and pH with the main aim of chemical modification for both electrodes. According to the obtained voltammograms, the best conditions were found at pH 10 and a sweep velocity of 250 mV/s as shown in Figures 5 and 6. | ![AZoJomo - The AZO Journal of Materials Online - Modification of VC, pH 10, sweep velocity 250 mV/s, 30 cycles, solution 1 mM [Ni(II)-L1]SO4, 0.1 M Na2SO4, sweep of potential from 0 to1000 mV.](http://www.azom.com/work/D59B4p6gjqU0Hqxh2qa1_files/image009.gif)
| | Figure 5. Modification of VC, pH 10, sweep velocity 250 mV/s, 30 cycles, solution 1 mM [Ni(II)-L1]SO4, 0.1 M Na2SO4, sweep of potential from 0 to1000 mV. | | ![AZoJomo - The AZO Journal of Materials Online - Modification of ITOP, pH 10, sweep velocity 250 mV/s, 30 cycles, solution 1 mM [Ni(II)-L]SO4, 0.1 M Na2SO4, sweep of potential from 0 to1000mV.](http://www.azom.com/work/D59B4p6gjqU0Hqxh2qa1_files/image011.gif)
| | Figure 6. Modification of ITOP, pH 10, sweep velocity 250 mV/s, 30 cycles, solution 1 mM [Ni(II)-L]SO4, 0.1 M Na2SO4, sweep of potential from 0 to1000mV. | | 


![AZoJomo - The AZO Journal of Materials Online - Thermograms of the complex [Ni(II)-L1]SO4](http://www.azom.com/work/D59B4p6gjqU0Hqxh2qa1_files/image007.gif)
![AZoJomo - The AZO Journal of Materials Online - Modification of VC, pH 10, sweep velocity 250 mV/s, 30 cycles, solution 1 mM [Ni(II)-L1]SO4, 0.1 M Na2SO4, sweep of potential from 0 to1000 mV.](http://www.azom.com/work/D59B4p6gjqU0Hqxh2qa1_files/image009.gif)
![AZoJomo - The AZO Journal of Materials Online - Modification of ITOP, pH 10, sweep velocity 250 mV/s, 30 cycles, solution 1 mM [Ni(II)-L]SO4, 0.1 M Na2SO4, sweep of potential from 0 to1000mV.](http://www.azom.com/work/D59B4p6gjqU0Hqxh2qa1_files/image011.gif)